Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the joints. Early detection is crucial for managing symptoms and slowing disease progression. Recognizing the early signs of rheumatoid arthritis can lead to timely treatment and a better quality of life. Below are the seven key signs of rheumatoid arthritis that individuals should be aware of:
Table of Contents
1. Persistent Joint Pain and Swelling
One of the hallmark symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis is persistent pain and swelling in the joints. Unlike osteoarthritis, which typically affects older individuals and is related to wear and tear, RA can occur at any age and is due to an autoimmune response. The pain often begins in the smaller joints, such as those in the fingers and toes, and may progress to larger joints like the knees, wrists, and elbows. This pain is typically symmetrical, meaning it affects both sides of the body equally.
How to Identify It?
- Duration: Pain and swelling lasting for more than six weeks.
- Location: Small joints first, then possibly spreading to larger joints.
- Consistency: Persistent and often worse in the morning or after periods of inactivity.
2. Morning Stiffness
Another early sign of rheumatoid arthritis is stiffness in the joints, particularly in the morning or after periods of inactivity. This stiffness can last for 30 minutes or more and is more prolonged than the typical stiffness experienced by people with osteoarthritis.
How to Identify It?
- Duration: Stiffness lasting more than 30 minutes.
- Timing: Most noticeable in the morning or after sitting for a long time.
- Relief: Movement and gentle exercise may help alleviate the stiffness.
3. Fatigue
Fatigue is a common but often overlooked symptom of rheumatoid arthritis. It can be severe and debilitating, impacting daily activities and overall quality of life. This fatigue is not just general tiredness; it is a profound lack of energy that doesn’t improve with rest.
How to Identify It?
- Severity: Intense and persistent, not relieved by sleep.
- Impact: Affects daily activities and mental well-being.
- Association: Often accompanied by other symptoms like loss of appetite and weight loss.
4. Fever and General Malaise
Low-grade fever and a general feeling of being unwell, or malaise, can also be signs of rheumatoid arthritis. These symptoms are often subtle and can be mistaken for a minor illness or infection.
How to Identify It?
- Temperature: Slightly elevated body temperature, typically less than 100.4°F (38°C).
- Feeling: General sense of discomfort and lack of well-being.
- Duration: Persistent and recurring, especially when other RA symptoms are present.
5. Joint Redness and Warmth
Inflammation caused by rheumatoid arthritis can lead to redness and warmth in the affected joints. This is due to increased blood flow to the inflamed areas.
How to Identify It?
- Appearance: Joints appear red and feel warm to the touch.
- Location: Common in small joints like fingers and toes.
- Consistency: Persistent and may worsen with activity.
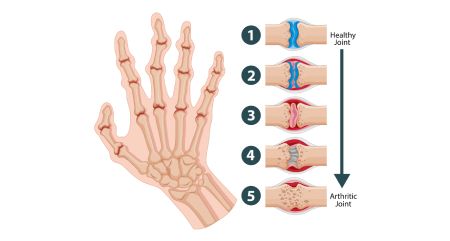
6. Decreased Range of Motion
As rheumatoid arthritis progresses, it can cause damage to the joints, leading to a decreased range of motion. This can make it difficult to perform everyday tasks, such as gripping objects, walking, or bending.
How to Identify It?
- Movement: Difficulty moving joints through their full range.
- Impact: Affects daily activities and overall mobility.
- Association: Often accompanied by joint pain and swelling.
7. Joint Deformity
In severe cases, rheumatoid arthritis can lead to visible joint deformities. This occurs due to prolonged inflammation and damage to the joint tissues. Deformities are more common in the later stages of the disease but can begin to develop relatively early in some individuals.
How to Identify It?
- Appearance: Joints may look misshapen or twisted.
- Location: Common in the hands and feet.
- Severity: Varies from mild changes to significant deformities affecting function.
Understanding the Importance of Early Diagnosis
Early diagnosis and treatment of rheumatoid arthritis are essential for managing the disease effectively. If you experience any of the above symptoms, it is important to seek medical advice promptly. A healthcare provider can perform a thorough evaluation, including physical examination, blood tests, and imaging studies, to diagnose rheumatoid arthritis and develop a treatment plan.
YOU MAY ALSO READ: Can Bipolar Disorder Be Self-Treated?
Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis
Effective management of rheumatoid arthritis involves a combination of medications, lifestyle changes, and supportive therapies. Common treatment options include:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), and biologics.
- Helps maintain joint function and mobility.
- Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management.
- Occupational therapy and counseling to cope with the emotional impact of the disease.
Conclusion.
Recognizing the early signs of rheumatoid arthritis is crucial for obtaining timely treatment and managing the disease effectively. Persistent joint pain, morning stiffness, fatigue, fever, joint redness, decreased range of motion, and joint deformity are key indicators to watch for. If you or a loved one are experiencing these symptoms, consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.

Leave a Comment