Pneumonia is a serious respiratory infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs. These air sacs may fill with fluid or pus, leading to symptoms such as cough, fever, chills, and difficulty breathing. Understanding the causes of pneumonia is crucial for prevention and treatment.
Table of Contents
Types of Pneumonia
Pneumonia can be classified based on the type of germ that causes the infection and where the infection was acquired.
Bacterial Pneumonia
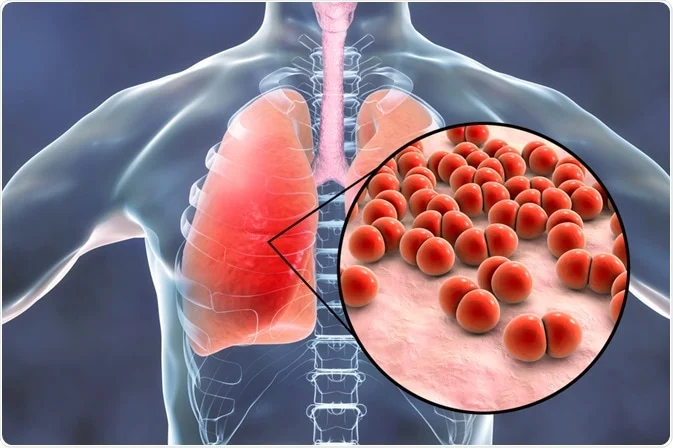
Bacterial pneumonia is the most common type and can be caused by various bacteria. The most frequent cause is Streptococcus pneumoniae. Other bacteria that can cause pneumonia include Haemophilus influenzae, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, and Legionella pneumophila. Bacterial pneumonia can occur on its own or after a person has had a cold or the flu.
Viral Pneumonia
Viral pneumonia is caused by viruses such as influenza, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and coronaviruses, including the one that causes COVID-19. Viral pneumonia is usually less severe than bacterial pneumonia, but it can still be serious, particularly in young children, older adults, and people with weakened immune systems.
Fungal Pneumonia
Fungal pneumonia is less common and typically affects people with weakened immune systems or chronic health problems. It is caused by fungi from soil or bird droppings. Common fungi that can cause pneumonia include Histoplasma, Coccidioides, and Cryptococcus.
Aspiration Pneumonia
Aspiration pneumonia occurs when a person inhales food, drink, vomit, or saliva into their lungs. This can happen if something disturbs the normal gag reflex, such as a brain injury, swallowing problem, or excessive use of alcohol or drugs.
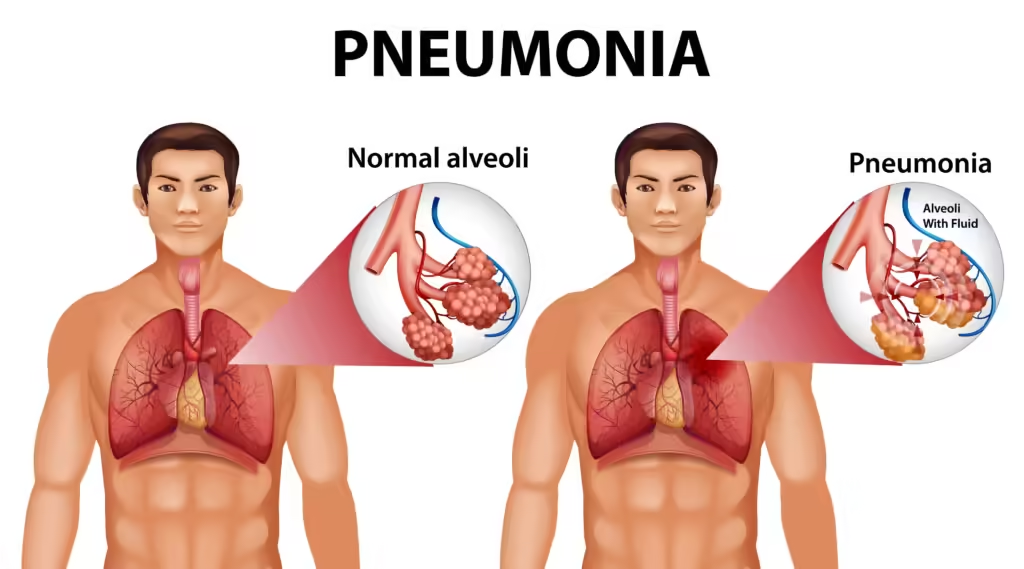
Common Causes and Risk Factors
Bacterial Infections
Bacteria are a leading cause of pneumonia. Streptococcus pneumoniae is the most common bacterial cause. Bacterial infections can develop after a viral infection like a cold or flu, making the body more susceptible to bacteria entering the lungs.
Viral Infections
Viruses such as influenza and RSV are common causes of viral pneumonia. The novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2), responsible for COVID-19, has also been a significant cause of viral pneumonia worldwide.
Weakened Immune System
People with weakened immune systems are at higher risk of developing pneumonia. This includes individuals with chronic illnesses such as HIV/AIDS, cancer, diabetes, and those who have undergone organ transplants. Immunocompromised individuals are more susceptible to infections by bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
Chronic Diseases
Chronic diseases like asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), heart disease, and diabetes can increase the risk of pneumonia. These conditions can weaken the body’s ability to fight off infections and can also cause complications that lead to pneumonia.
Smoking
Smoking damages the lungs’ natural defenses against respiratory infections, increasing the risk of pneumonia. Smokers are more susceptible to infections because smoking impairs the function of cilia, the tiny hair-like structures that help clear mucus and debris from the lungs.
Age
Age is a significant risk factor for pneumonia. Young children under the age of 2 and adults over the age of 65 are at higher risk. The immune system’s ability to fight infections is not fully developed in young children and can weaken with age in older adults.
Hospitalization
Hospitalized patients, especially those in intensive care units (ICUs) or on ventilators, are at increased risk of pneumonia. Hospital-acquired pneumonia can be caused by bacteria that are more resistant to antibiotics, making it more challenging to treat.
Environmental and Occupational Factors
Exposure to certain environmental or occupational hazards can increase the risk of pneumonia. These include inhaling chemicals, dust, or toxic fumes, which can irritate the lungs and make them more susceptible to infection.
YOU MAY ALSO READ: What Happens During Menopause?
Preventing Pneumonia
Vaccination
Vaccines are available to prevent some types of pneumonia. The pneumococcal vaccine can protect against Streptococcus pneumoniae, and the influenza vaccine can help prevent viral pneumonia caused by the flu. Vaccination is particularly important for young children, older adults, and people with chronic health conditions.
Good Hygiene Practices
Maintaining good hygiene can help prevent the spread of infections that cause pneumonia. Regular hand washing, covering your mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing, and avoiding close contact with sick individuals can reduce the risk of respiratory infections.
Healthy Lifestyle
A healthy lifestyle can strengthen the immune system and reduce the risk of pneumonia. This includes eating a balanced diet, getting regular exercise, staying hydrated, and getting enough sleep. Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption is also crucial for lung health.
Regular Medical Checkups
Regular medical checkups can help detect and manage chronic health conditions that can increase the risk of pneumonia. Managing conditions like asthma, COPD, and diabetes effectively can reduce the likelihood of developing pneumonia.
Conclusion.
Pneumonia is caused by various germs, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi, as well as by inhaling foreign substances into the lungs. Risk factors such as a weakened immune system, chronic diseases, smoking, age, and environmental factors can increase susceptibility to pneumonia. Preventative measures, including vaccination, good hygiene practices, and a healthy lifestyle, are essential to reduce the risk of pneumonia.

Leave a Comment