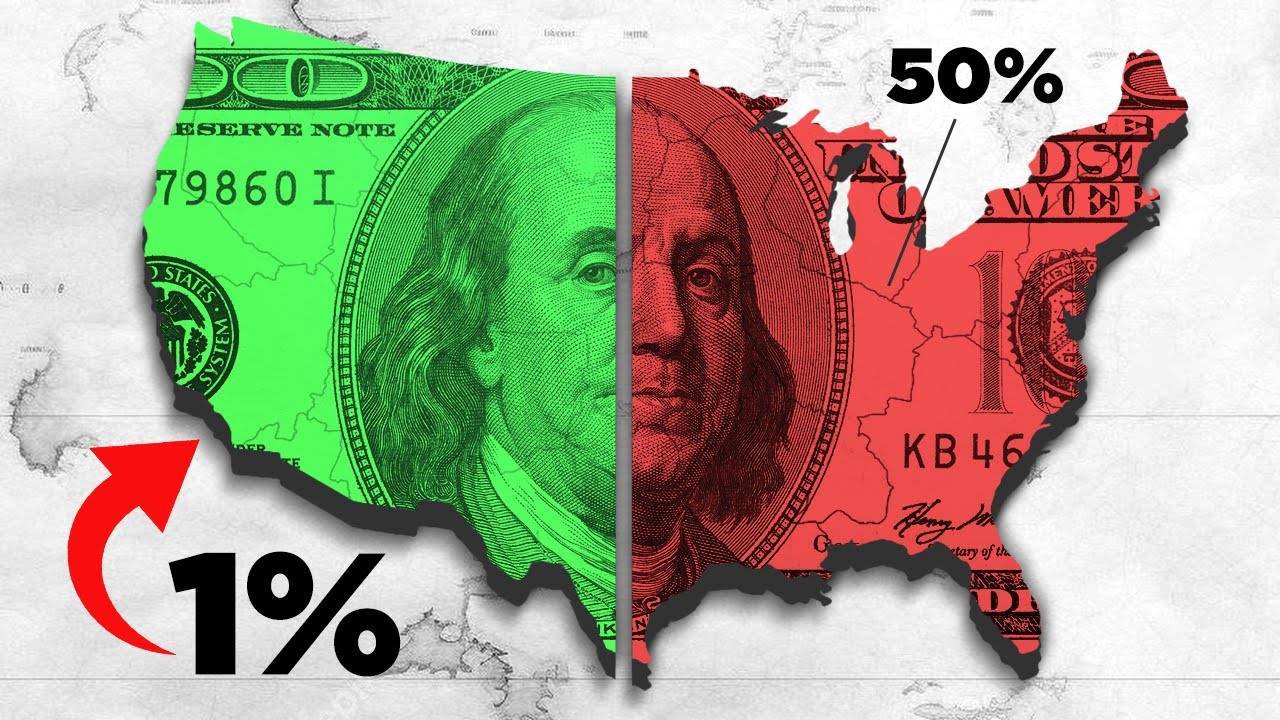
Income Inequality of America
Income inequality in America has become a significant and enduring issue that touches nearly every aspect of society. Over the past few decades, the gap between the wealthy and the rest of the population has widened substantially, leading to profound economic, social, and political implications. This article delves into the causes of income inequality, its impacts on various facets of society, and potential solutions to address this pressing concern.
Table of Contents
Understanding Income Inequality
Income inequality refers to the unequal distribution of income among individuals or households within a society. In the context of the United States, this phenomenon has been on the rise since the 1970s. According to data from the U.S. Census Bureau, the top 1% of earners in the U.S. now command a significantly larger share of the nation’s income compared to previous decades.
Several factors contribute to income inequality:
- Technological Advancement: The rapid pace of technological innovation has transformed the economy, leading to the automation of many jobs and creating new industries that benefit a select few with specialized skills.
- Globalization: Increased trade and globalization have shifted certain industries overseas, reducing job opportunities for low-skilled workers in the U.S. while benefiting multinational corporations and skilled workers.
- Decline in Unionization: The decline of labor unions has weakened the bargaining power of workers, particularly in industries like manufacturing, where unions historically played a crucial role in securing fair wages and benefits.
- Policy Changes: Changes in tax policies, deregulation, and reductions in social safety nets have disproportionately favored the wealthy, exacerbating income disparities.
Impacts of Income Inequality
The effects of income inequality extend beyond economic disparities and impact various aspects of society:
- Health Disparities: Research shows a correlation between income inequality and health outcomes, with lower-income individuals experiencing higher rates of chronic illnesses and reduced life expectancy.
- Educational Opportunities: Income inequality can limit access to quality education, perpetuating a cycle of disadvantage for children from low-income families.
- Social Mobility: Rising income inequality has been linked to decreased social mobility, making it harder for individuals from disadvantaged backgrounds to move up the economic ladder.
- Political Influence: Wealthy individuals and corporations wield significant political influence through lobbying and campaign contributions, potentially distorting democratic processes.
Addressing Income Inequality
Addressing income inequality requires a multifaceted approach involving policy interventions, economic reforms, and societal changes:
- Progressive Taxation: Implementing progressive tax policies that increase taxes on the wealthy can help redistribute wealth and fund social programs aimed at reducing inequality.
- Investment in Education: Enhancing access to quality education, particularly for underserved communities, can empower individuals to break the cycle of poverty and inequality.
- Support for Workers: Strengthening labor rights, promoting unionization, and ensuring fair wages and benefits for all workers are essential steps toward reducing income disparities.
- Healthcare Reform: Access to affordable healthcare is critical for reducing health disparities associated with income inequality.
- Addressing Structural Barriers: Policies that address discrimination based on race, gender, or other factors can help create a more equitable society.
- Inclusive Economic Growth: Promoting inclusive economic growth that benefits all segments of society, rather than just the wealthy few, should be a priority.
Conclusion.
Income inequality in America is a complex and persistent challenge with far-reaching consequences. Tackling this issue requires a concerted effort from policymakers, businesses, and civil society to enact meaningful reforms that promote fairness, equality of opportunity, and social cohesion. By addressing the root causes of income inequality and implementing targeted interventions, we can work towards building a more equitable and inclusive society where everyone has the chance to thrive.