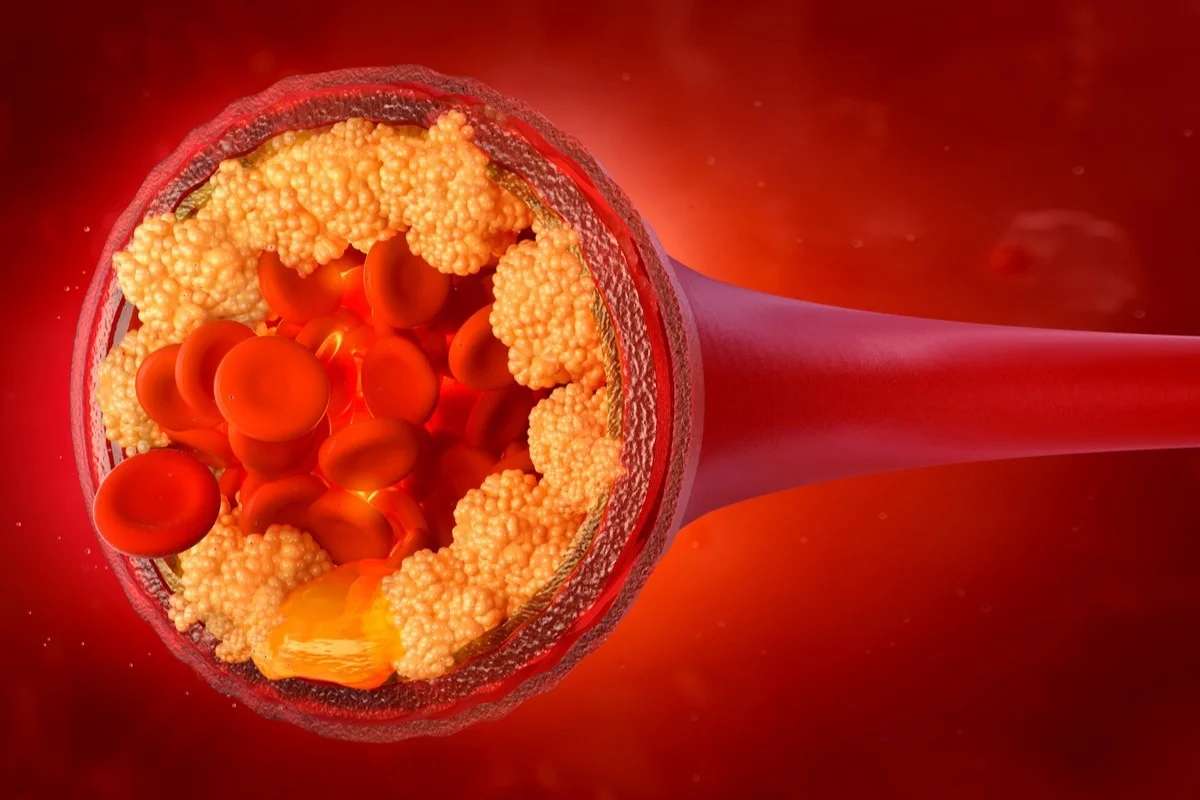
LDL Cholesterol, often referred to as “bad” cholesterol, plays a significant role in your body’s overall health. While cholesterol itself is a necessary substance used for building cells and producing certain hormones, an elevated level of LDL cholesterol can lead to serious health issues, particularly cardiovascular diseases.
Table of Contents
Causes of High LDL Cholesterol
High LDL cholesterol can result from a combination of factors including genetics, lifestyle choices, and underlying health conditions. Here are some common causes:
Diet
A diet high in saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol can raise your LDL levels. Foods such as red meat, full-fat dairy products, and processed foods are the primary culprits.
Lack of Physical Activity
A sedentary lifestyle can lead to weight gain, which is associated with higher LDL cholesterol and lower High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, the “good” cholesterol.
Obesity
Being overweight tends to increase your LDL cholesterol level while decreasing your HDL cholesterol level. It also elevates your risk of developing other health issues.
Smoking
Smoking cigarettes can damage your blood vessels, making them more susceptible to the buildup of fatty deposits. It also lowers HDL cholesterol levels.
Genetics
Familial hypercholesterolemia is a genetic condition that causes very high LDL levels and increases the risk of early heart disease.
Medical Conditions
Conditions such as diabetes, hypothyroidism, and kidney disease can lead to elevated LDL cholesterol levels.
YOU MAY ALSO READ: Is Pneumonia Serious or Not?
Health Risks Associated with High LDL Cholesterol
High LDL cholesterol is a major risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, including:
Atherosclerosis
This condition occurs when LDL cholesterol builds up in the walls of arteries, forming plaques that can restrict blood flow. Atherosclerosis can lead to serious complications like heart attacks and strokes.
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
High LDL cholesterol can cause the coronary arteries to narrow, reducing blood flow to the heart muscle. This can result in chest pain (angina), heart attacks, and other heart-related issues.
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)
Elevated LDL levels can also affect arteries in the limbs, leading to PAD. This condition can cause pain and numbness in the legs and increase the risk of infection.
Stroke
If a plaque ruptures in the brain’s arteries, it can cause a stroke. Strokes can lead to permanent brain damage and other serious complications.

Diagnosing High LDL Cholesterol
Diagnosing high LDL cholesterol involves a simple blood test called a lipid panel or lipid profile. This test measures your total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, and triglycerides. Here’s what to expect:
Preparation
You may be asked to fast for 9-12 hours before the test to ensure accurate results.
Blood Sample Collection
A healthcare professional will draw blood from a vein, typically in your arm.
Analysis
The blood sample is analyzed in a laboratory, and results are usually available within a few days.
Managing and Lowering High LDL Cholesterol
Effective management of high LDL cholesterol involves lifestyle changes, medications, and regular monitoring. Here are some strategies to consider:
Dietary Changes
Adopting a heart-healthy diet can significantly lower LDL cholesterol levels. Focus on:
- Rich in fiber and antioxidants, they help reduce LDL cholesterol.
- Oats, barley, and other whole grains contain soluble fiber, which can lower LDL levels.
- Replace saturated and trans fats with unsaturated fats found in olive oil, avocados, and nuts.
- Opt for lean sources of protein such as fish, poultry, and legumes.
Regular Exercise
Engaging in regular physical activity can help lower LDL cholesterol and raise HDL cholesterol. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week.
Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight can improve your cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of related health issues.
Quit Smoking
If you smoke, quitting can improve your HDL cholesterol levels and overall heart health.
Medications
In some cases, lifestyle changes may not be enough to lower LDL cholesterol. Medications such as statins, bile acid sequestrants, and cholesterol absorption inhibitors may be prescribed.
Regular Monitoring
Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider are essential for monitoring your cholesterol levels and adjusting your treatment plan as needed.
Conclusion
High LDL cholesterol poses significant risks to your cardiovascular health, but with proper management and lifestyle changes, it is possible to lower your LDL levels and reduce the associated risks. By understanding the causes, health risks, and management strategies, you can take proactive steps toward maintaining healthy cholesterol levels and improving your overall well-being.

Leave a Comment