What is the Main Cause of Myeloma?
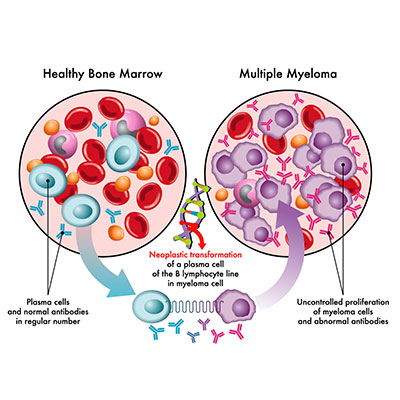
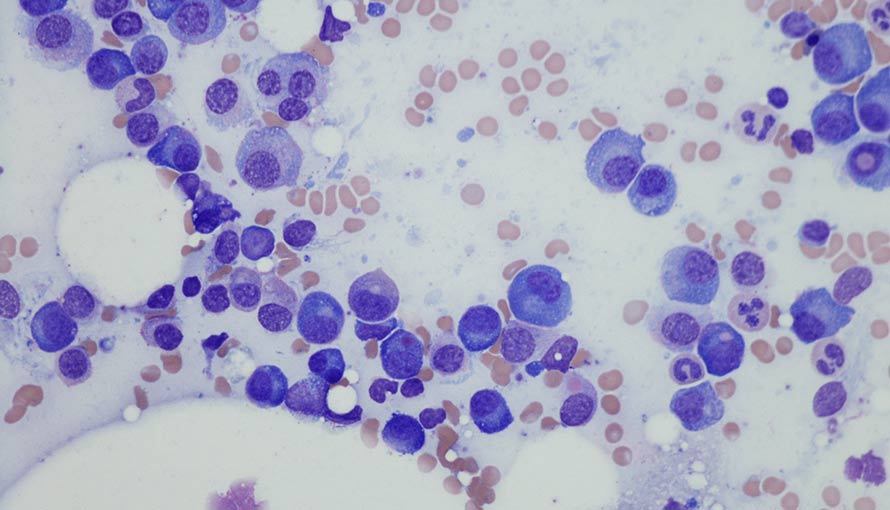
Myeloma, also known as multiple myeloma, is a type of cancer that originates in the plasma cells of the bone marrow. Plasma cells are essential to the immune system, producing antibodies to fight infections. However, in myeloma, these cells become cancerous and proliferate uncontrollably. Understanding the causes of myeloma is critical for advancing treatment and potentially finding a cure. This article delves into the main causes and risk factors associated with this disease.
Table of Contents
Genetic Factors
Genetic Mutations and Myeloma
Genetic mutations play a significant role in the development of myeloma. Researchers have identified several genetic abnormalities that contribute to the onset of this disease. Chromosomal translocations, where segments of chromosomes swap places, are common in myeloma. Specifically, translocations involving the immunoglobulin heavy chain (IgH) gene on chromosome 14 are frequently observed. These translocations can result in the activation of oncogenes, which promote the growth of cancer cells.
Inherited Genetic Susceptibility
While most cases of myeloma are not directly inherited, there is evidence suggesting a familial predisposition. Individuals with a family history of myeloma or other blood cancers have a higher risk of developing the disease. Studies have shown that certain genetic polymorphisms, or variations in DNA sequence, may increase susceptibility to myeloma. These findings underscore the importance of genetic factors in the disease’s etiology.
Environmental Factors
Exposure to Radiation
Exposure to high levels of radiation is a known risk factor for many cancers, including myeloma. Ionizing radiation, such as that from atomic bomb explosions or radiation therapy for other cancers, can damage DNA and lead to cancerous changes in cells. Although radiation-induced myeloma is relatively rare, it highlights the impact of environmental factors on disease development.
Chemical Exposure
Exposure to certain chemicals has also been linked to an increased risk of myeloma. Benzene, a chemical found in industrial settings and cigarette smoke, is a well-established carcinogen. Prolonged exposure to pesticides, herbicides, and other organic solvents may also elevate the risk. These chemicals can cause genetic mutations and disrupt normal cell function, contributing to the onset of myeloma.
Immune System Dysfunction
Chronic Immune Stimulation
Chronic stimulation of the immune system is another factor implicated in the development of myeloma. Conditions that cause persistent immune activation, such as chronic infections or autoimmune diseases, can increase the risk. Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS), a condition characterized by an abnormal increase in plasma cells, is considered a precursor to myeloma. Although MGUS is benign, it can progress to myeloma in some individuals, indicating a link between immune system dysfunction and the disease.
Inflammatory Conditions
Inflammatory conditions, such as obesity and chronic inflammation, have been associated with an increased risk of myeloma. Obesity, in particular, is linked to higher levels of inflammatory cytokines, which can promote cancer development. Chronic inflammation creates an environment conducive to genetic mutations and cancer cell proliferation.
YOU MAY ALSO READ: Can Monkeypox be cured?
Age and Demographic Factors
Age-Related Risks
Age is one of the most significant risk factors for myeloma. The disease is rare in individuals under 40, with the majority of cases occurring in those over 60. The reasons for this age-related risk are not fully understood, but it may be related to the accumulation of genetic mutations and decreased immune function with age.
Ethnic and Gender Disparities
Myeloma incidence varies across different demographic groups. African Americans have a higher risk of developing myeloma compared to other ethnicities. The reasons for this disparity are not entirely clear but may involve genetic and environmental factors. Additionally, men are slightly more likely to develop myeloma than women, suggesting potential hormonal influences on disease risk.
Lifestyle Factors
Diet and Exercise
While the direct impact of diet and exercise on myeloma risk is still being studied, maintaining a healthy lifestyle is generally beneficial for cancer prevention. Diets rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, coupled with regular physical activity, support overall immune health and may reduce the risk of various cancers, including myeloma.
Smoking and Alcohol Consumption
Smoking is a well-known risk factor for many cancers, including myeloma. The carcinogenic compounds in tobacco smoke can damage DNA and promote cancer development. Similarly, excessive alcohol consumption has been linked to an increased risk of myeloma. Limiting these behaviors can help reduce the risk of developing the disease.
Conclusion.
The main causes of myeloma are multifaceted, involving a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Genetic mutations and familial predisposition play crucial roles, while environmental exposures to radiation and chemicals further elevate risk. Immune system dysfunction and demographic factors such as age, ethnicity, and gender also contribute to disease development. By understanding these causes, we can better tailor prevention strategies and improve treatment outcomes for those affected by myeloma.





One Comment